- This wiki is out of date, use the continuation of this wiki instead
Operators
From FenixWiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Revision as of 00:18, 30 May 2007 (edit) Sandman (Talk | contribs) m (→Memory) ← Previous diff |
Current revision (15:52, 19 August 2008) (edit) (undo) Sandman (Talk | contribs) m (→Bitwise) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| | ''Operator'' || - ''Description'' | | ''Operator'' || - ''Description'' | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| - | | Type || - Get the [[ProcessTypeID]] of a [[ProcessType]]. | + | | Type || - Get the [[ProcessTypeID]] of a [[ProcessType]] or define a new [[datatype]]. See [[Type]]. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . <small>(period)</small> || - Element access. <code><struct>.<element></code>. In case of a struct array, if no arrayelement is specified, it points to [0] (see [[#Example|example]]). | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| Line 47: | Line 49: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ~ || - BNOT. | | ~ || - BNOT. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | << || - Bitshift left, causes bits to move left a certain number of positions. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | >> || - Bitshift left, causes bits to move right a certain number of positions. | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| Line 60: | Line 66: | ||
| == Example == | == Example == | ||
| <pre> | <pre> | ||
| - | + | Type _point | |
| + | int x; | ||
| + | int y; | ||
| + | End | ||
| + | |||
| Global | Global | ||
| int int_1 = 1; | int int_1 = 1; | ||
| Line 72: | Line 82: | ||
| byte b_5 = 5; | byte b_5 = 5; | ||
| byte b_12 = 12; | byte b_12 = 12; | ||
| + | Struct Person[9] | ||
| + | string name; | ||
| + | int age; | ||
| + | End | ||
| + | _point myPoint; | ||
| + | End | ||
| + | |||
| + | Process Main() | ||
| Begin | Begin | ||
| Line 117: | Line 135: | ||
| // -------- ~ | // -------- ~ | ||
| // 11110011 = 243 | // 11110011 = 243 | ||
| + | |||
| + | person.name = "Mies"; // these are the same | ||
| + | person[0].name = "Mies"; // | ||
| + | |||
| + | person[1].name = "Aap"; | ||
| + | person[2].name = "Noot"; | ||
| + | // ...etc... | ||
| + | person[9].name = "Last person"; // last array element | ||
| + | |||
| + | setXY(&myPoint); | ||
| Repeat | Repeat | ||
| frame; | frame; | ||
| - | Until(key( | + | Until(key(_ESC)) |
| + | End | ||
| + | |||
| + | Function int setXY(_point* p) | ||
| + | Begin | ||
| + | p.x = 3; // this is actually (*p).x = 3, but . can be used like this | ||
| + | p.y = 5; // this is actually (*p).y = 5, but . can be used like this | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| End | End | ||
| </pre> | </pre> | ||
| - | Used in example: [[say]]() | + | Used in example: [[say]](), [[key]](), [[Global]], [[Type]], [[Struct]], [[Array]], [[Pointer]], [[period]] |
| This will result in something like:<br> | This will result in something like:<br> | ||
| - | + | {{Image | |
| + | | image = Operators.png | ||
| + | | caption = operator results | ||
| + | }} | ||
Current revision
Contents |
[edit] List of Operators
[edit] General
| Operator | - Description |
| Type | - Get the ProcessTypeID of a ProcessType or define a new datatype. See Type. |
| . (period) | - Element access. <struct>.<element>. In case of a struct array, if no arrayelement is specified, it points to [0] (see example).
|
[edit] Maths
| Operator | - Description |
| + | - Addition. |
| - | - Deduction |
| * | - Multiplication. |
| / | - Division. |
[edit] Logic
| Operator | - Description |
| || | - OR. One or the other or both. |
| && | - AND. Both. |
| ^^ | - XOR. One or the other, but not both. |
| ! | - NOT. |
[edit] Bitwise
(Logical operation per bit.)
| Operator | - Description |
| | | - BOR. One or the other or both. |
| & | - BAND. Both. |
| ^ | - BXOR. One or the other, but not both. |
| ~ | - BNOT. |
| << | - Bitshift left, causes bits to move left a certain number of positions. |
| >> | - Bitshift left, causes bits to move right a certain number of positions. |
[edit] Memory
| Operator | - Description |
| & | - OFFSET. Get the memory address of a variable. See pointer. |
| * | - POINTER. Get access to the variable a pointer is pointing to. See pointer. |
[edit] Example
Type _point
int x;
int y;
End
Global
int int_1 = 1;
int int_3 = 3;
int int_4 = 4;
int someint = -5;
String somestring = "AAP";
String anotherstring = "BEER";
byte somebyte = 6;
signed byte sbyte = -2;
byte b_5 = 5;
byte b_12 = 12;
Struct Person[9]
string name;
int age;
End
_point myPoint;
End
Process Main()
Begin
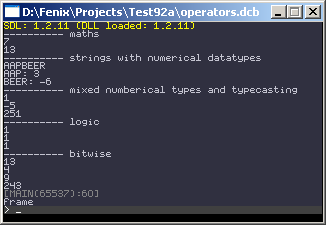
say("---------- maths");
say(int_3 + int_4);
say(int_3 * int_4 + 1);
say("---------- strings with numerical datatypes");
say(somestring + anotherstring);
say(somestring + ": " + int_3);
say(anotherstring + ": " + int_3*sbyte);
say("---------- mixed numberical types and typecasting");
say(somebyte+someint);
say((signed byte)someint);
say((unsigned byte)someint);
say("---------- logic");
say(int_1&&int_4);
say(int_4==int_3+int_1);
say(!(somestring==anotherstring));
say("---------- bitwise");
say(b_5|b_12); // 00000101
// 00001100
// -------- |
// 00001101 = 13
say(b_5&b_12); // 00000101
// 00001100
// -------- &
// 00000100 = 4
say(b_5^b_12); // 00000101
// 00001100
// -------- ^
// 00001001 = 9
say(~b_12); // 00001100
// -------- ~
// 11110011 = 243
person.name = "Mies"; // these are the same
person[0].name = "Mies"; //
person[1].name = "Aap";
person[2].name = "Noot";
// ...etc...
person[9].name = "Last person"; // last array element
setXY(&myPoint);
Repeat
frame;
Until(key(_ESC))
End
Function int setXY(_point* p)
Begin
p.x = 3; // this is actually (*p).x = 3, but . can be used like this
p.y = 5; // this is actually (*p).y = 5, but . can be used like this
return 0;
End
Used in example: say(), key(), Global, Type, Struct, Array, Pointer, period
This will result in something like:
|
