- This wiki is out of date, use the continuation of this wiki instead
Fget angle
From FenixWiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Revision as of 12:12, 11 July 2007 (edit) Sandman (Talk | contribs) m (→Example) ← Previous diff |
Current revision (15:11, 1 March 2008) (edit) (undo) Sandman (Talk | contribs) m (→Example) |
||
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| == Example == | == Example == | ||
| <pre> | <pre> | ||
| - | Program angling; | ||
| Const | Const | ||
| screen_width = 320; | screen_width = 320; | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
| screen_fps = 60; | screen_fps = 60; | ||
| screen_frameskip = 0; | screen_frameskip = 0; | ||
| + | End | ||
| + | |||
| Global | Global | ||
| int distance; | int distance; | ||
| int tempID; | int tempID; | ||
| + | End | ||
| + | |||
| + | Process Main() | ||
| Begin | Begin | ||
| Line 79: | Line 83: | ||
| It could look something like:<br> | It could look something like:<br> | ||
| - | + | {{Image | |
| + | | image = fget_angle.png | ||
| + | | caption = [[fget_angle]]() and [[fget_dist]]() | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Funcbox | ||
| + | | category = Math | ||
| + | }} | ||
Current revision
Contents |
[edit] Definition
INT fget_angle ( <INT pointA-X> , <INT pointA-Y> , <INT pointB-X> , <INT pointB-Y> )
Returns the angle between two certain points. The returned angle will be ranging from 0 to 360000 (0-360º).
[edit] Parameters
| INT pointA-X | - The X-coordinate of point A. |
| INT pointA-Y | - The Y-coordinate of point A. |
| INT pointB-X | - The X-coordinate of point B. |
| INT pointB-Y | - The Y-coordinate of point B. |
[edit] Returns
INT : The angle between point A and point B.
[edit] Notes
The angle value returned by this function is in thousandths of degrees, as most angles within Fenix are.
[edit] Example
Const
screen_width = 320;
screen_height = 200;
screen_depth = 8;
screen_fps = 60;
screen_frameskip = 0;
End
Global
int distance;
int tempID;
End
Process Main()
Begin
// Set the screen mode
set_mode(screen_width,screen_height,screen_depth);
set_fps(screen_fps,screen_frameskip);
// Change this to see what happens
resolution = 100;
// Create mouse graph, assign to mouse.graph
mouse.graph = new_map(20,20,screen_depth);
map_clear(0,mouse.graph,rgb(255,0,0));
// Create arrow, assign to graph
graph = new_map(30,30,screen_depth);
drawing_map(0,graph);
drawing_color(rgb(0,255,0));
draw_line( 0,29,29,30/2);
draw_line( 0, 0,30,30/2);
// Set position
x = screen_width /2 * resolution;
y = screen_height/2 * resolution;
// Display distance
write(0,0,0,0,"Distance:");
write_int(0,60,0,0,&distance);
// Always point to the mouse
Repeat
// Get the angle and distance between this process' coordinates and those of the mouse.
angle = fget_angle(x,y,mouse.x*resolution,mouse.y*resolution);
distance = fget_dist (x,y,mouse.x*resolution,mouse.y*resolution);
frame;
Until(key(_esc))
End
Used in example: set_mode(), new_map(), map_clear(), drawing_map(), drawing_color(), draw_line(), write(), write_int(), fget_angle(), fget_dist(), resolution, mouse, graph, x, y, angle
This example could also be done with get_angle(), but that would be more work.
It could look something like:
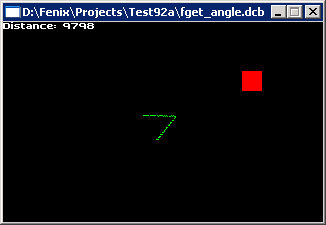
|
| Math Functions | |
| • Abs() • Acos() • Asin() • Atan() • Cos() • Fget_angle() • Fget_dist() • Get_distx() • Get_disty() • Pow() • Rand() • Rand_seed() • Sin() • Sqrt() • Tan() • | |
